Introduction
Getting bitten by a dog can be a traumatic experience, especially if it occurs on your own property. As a dog owner, you may be wondering if you’re legally liable if your pooch bites someone while on your land. The short answer is – it depends. Dog bite laws vary by state and municipality, but there are some general principles that apply. In this article, we’ll walk through the key factors in determining liability, including location, provocation, prior incidents, and resulting injuries. We’ll also discuss steps you can take to protect yourself and your furry friend. While no one wants to think about their dog biting someone, it’s important to understand your potential exposure so you can take appropriate precautions.
Legal Principles
Dog bite laws generally fall into two legal categories – negligence laws and strict liability laws. Negligence laws require the victim to prove the dog owner was negligent in preventing the bite. This means proving the owner knew or should have known the dog might bite and failed to take reasonable precautions. Strict liability laws on the other hand focus simply on the action itself, not the owner’s level of care or intent. With strict liability, if the dog bites someone, the owner is liable regardless of precautions taken.
Most states apply a negligence standard to bites occurring in public spaces. To hold the owner liable, the victim must show the owner failed to properly restrain the dog or knew the dog had a history of biting yet took no precautions. However, when a dog bites on the owner’s property, most states impose strict liability. This means victims don’t need to prove negligence – if the bite occurred on the owner’s property, the owner is automatically liable regardless of previous precautions.
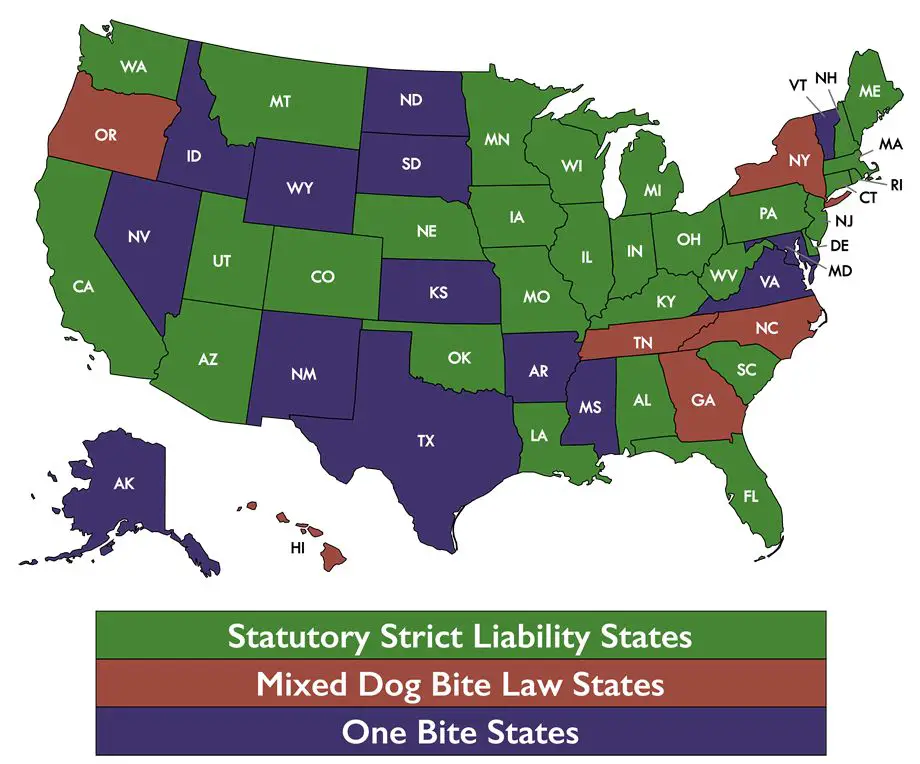
A minority of states do still apply a negligence standard even to bites on an owner’s property. But strict liability is generally the prevailing rule, given the greater ability of owners to control their dogs in their own homes and yards. So if your dog bites someone in your home or yard, you will likely be considered liable regardless of the steps taken to restrain your dog.
On Your Property
If your dog bites someone while on your property, you may be liable for the victim’s injuries. Homeowners and renters insurance policies often provide coverage in these situations. However, there are several factors that determine your legal responsibility:
- Was the victim legally allowed to be on your property? For example, if they were trespassing, you likely have less liability.
- Did the victim provoke your dog or ignore warnings about your dog? If so, their actions may reduce your liability.
- Does your dog have a history of aggression or biting incidents? Prior known behavior increases liability.
- Did you take reasonable precautions to restrain your dog or warn visitors about your dog? Taking safety measures helps reduce liability.
- What were the age, condition, and abilities of the victim? Minors and those with disabilities may elicit greater liability.
In many states, dog owners are strictly liable for bites occurring on their property. Consult a personal injury attorney to determine your liability and insurance protections.
In a Public Space
If your dog bites someone in a public area like a park, sidewalk, or street, you may be liable for any injuries and damages that occur. This is because pet owners generally have a duty to prevent their dogs from harming others when in public.
If your dog bites someone in a public space, the injured person only needs to prove you were legally responsible for controlling the dog and you failed to properly restrain it or prevent the bite. You may argue the victim provoked the dog, but mere provocation is often insufficient to avoid liability in a public setting.
Additionally, you may be held responsible even if you did not know your dog had aggressive tendencies. When in public, pet owners are expected to have control of their dogs.
However, if the victim was trespassing on private property at the time of the bite, your liability may be reduced or eliminated depending on the circumstances.
Overall, legal responsibility generally falls upon dog owners when bites occur in public areas. Having homeowner’s or renter’s insurance with liability coverage is wise to protect yourself financially if a dog bite happens away from your property.
Provocation
Whether the victim provoked the dog and contributed to the attack can affect liability. Provocation is a mitigating circumstance that may reduce an owner’s responsibility, especially if the victim trespassed or abused the dog. However, the owner must still exercise reasonable care to prevent foreseeable harm.
Actions by the victim that may constitute provocation include trespassing, teasing, startling, harming, or threatening the dog. But provoked bites often still result in some liability for the owner if a reasonable person would expect the dog to attack under the circumstances. The victim’s provocation must be significant enough to justify the dog’s reaction.
If the victim had no valid reason to provoke the dog, the owner will likely retain full liability. But if the provocation was extreme or egregious, the owner’s responsibility may be limited or eliminated. The specific circumstances and jurisdiction will determine how provocation influences liability.
Prior Incidents
A dog’s history of aggression will often play an important role in determining liability after a biting incident. If your dog has exhibited aggressive behavior or bitten before, it shows you were aware of the dog’s dangerous propensities. This makes it much more difficult for you to claim the incident was unforeseeable.
Any prior incidents of biting or aggression should have prompted you to take measures to prevent further occurrences. This may include muzzling your dog when guests are present, keeping it confined while you are not home, posting warning signs on your property, or other reasonable precautions. If your dog then bites again despite your knowledge of its tendencies, your failure to take adequate precautions will make it very challenging to avoid liability.
The impact of your dog’s history depends partially on the circumstances and severity of the prior incidents. A minor nip as a puppy has less significance than a vicious attack last year. But in general, any indications of aggression in your dog’s past will weaken arguments that you could not have reasonably predicted the biting. Be prepared for plaintiffs to thoroughly investigate your dog’s background through veterinary records, animal control reports, and witness accounts.
Injuries

The extent of injuries caused by a dog bite often determines the liability and compensation in a dog bite case. More severe injuries generally warrant higher compensation. Common dog bite injuries include:
- Lacerations – Deep cuts and tears in the skin caused by the dog’s teeth.
- Nerve Damage – Injury to nerves that may result in loss of feeling or use of affected body parts.
- Scarring – Permanent marks left on the skin after a wound is healed. Severe scarring can be disfiguring.
- Infections – Bacteria from a dog’s mouth enters wounds and causes infections like rabies, tetanus, or MRSA.
- Broken Bones – Fractures and broken bones, especially in hands, arms, and fingers from warding off an attack.
- Puncture Wounds – Small, deep holes caused by each tooth as the dog bites down.
- Torn Muscles/Tendons – Damage to muscles and tendons from the dog’s teeth and force of bite.
- Emotional Distress – Psychological trauma like PTSD, especially in children.
More severe injuries increase liability, and may warrant higher compensation in a dog bite lawsuit. Permanent damage like disfigurement or disability can greatly impact the settlement amount.
Protecting Yourself from Liability
There are several steps dog owners can take to reduce the risk of liability if their dog bites someone:
-
Obedience training – A well-trained dog is less likely to bite. Invest in professional training to teach your dog basic obedience commands and proper socialization.
-
Leash your dog – Keep your dog leashed and under control when in public spaces. Even friendly dogs can be provoked to bite by a stranger.
-
Beware of triggers – Learn your dog’s triggers that may cause aggressive behavior like fear, pain, or protecting territory.
-
Post warning signs – Post clearly visible “Beware of Dog” signs around your property to alert people.
-
Muzzle – Use a basket-style muzzle to prevent biting while allowing your dog to pant and drink.
-
Secure your property – Install secure fencing and gates around your yard. Keep garage doors closed.
-
Supervise interactions – Closely supervise your dog around strangers, children, or service people and intervene at signs of agitation.
-
Consider your breed – Some breeds like pit bulls face breed-specific legislation. Take proper precautions based on your dog’s breed traits.
Taking preventative measures can help protect both your dog and those interacting with them, while minimizing liability risks as a dog owner.
Insurance
Having the right insurance is important to protect yourself financially in case your dog bites someone. Here are some dog bite liability insurance options to consider:
- Homeowners or renters insurance – Most standard policies cover dog bite liability, but coverage amounts and exclusions vary. Make sure your policy covers dog bites and has adequate limits.
- Umbrella insurance – Extra liability coverage in addition to homeowners/renters insurance. Provides an extra layer of protection.
- Dog liability insurance – Specialized policies just for dog bite liability, often required for specific dog breeds. Covers defense costs in addition to damages.
Also consider increasing your liability limits if you own a large dog breed prone to biting. Consulting with an insurance agent can help you determine the right amount and type of coverage for your situation.
Conclusion

In summary, dog owners can be held liable if their dog bites someone, even if it occurs on their own property. The extent of liability depends on the circumstances and jurisdiction. Some key recommendations for dog owners are:
- Train your dog and keep it confined if it has shown aggressive tendencies.
- Post clear warning signs if you have a dog that may bite.
- Consider getting liability insurance in case an incident does occur.
- Always keep your dog supervised when guests are over.
- Use secure fencing, gates, and leashes when taking your dog into public areas.
- Consult with a dog trainer or animal behaviorist if your dog has a history of biting people.
While owners should take reasonable precautions, it’s also important to educate children and adults on safe behavior around dogs. With thoughtful measures taken by both owners and non-owners, many dog bites can be prevented.