Introduction
Chocolate contains substances like theobromine and caffeine that can be toxic to dogs when ingested. The severity of chocolate toxicity depends on the amount and type of chocolate consumed relative to the dog’s size and weight. While small amounts may cause vomiting and diarrhea, large amounts of chocolate can cause serious issues like seizures, irregular heart rhythms, and even death.
This article explores how chocolate impacts dogs, the signs of chocolate poisoning, and whether it can lead to kidney failure for affected dogs. We’ll also discuss prevention methods and treatment options for chocolate toxicity.
Why Chocolate is Toxic to Dogs
Chocolate contains compounds called theobromine and caffeine. Unlike humans, dogs do not efficiently metabolize these chemicals due to a lack of necessary enzyme pathways[1]*. The theobromine and caffeine accumulate in the dog’s body and can lead to chocolate poisoning or toxicity if enough is ingested.
Theobromine and caffeine belong to a chemical family called methylxanthines. Methylxanthines act as stimulants that increase heart rate, muscle contractions, and the nervous system[2]*. Normal amounts of methylxanthines can be metabolized by humans and dogs. However, dogs only have the pathways to break down small doses, allowing toxic levels of these chemicals to build up if they eat chocolate.
Of the two methylxanthines, theobromine is the primary contributor to chocolate’s toxicity for dogs. While small amounts of theobromine have mild diuretic effects, at higher doses it can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle tremors, heart arrhythmias, seizures and death.
[1]* https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/chocolate-poisoning-in-dogs
[2]* https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1215566/
Amount of Chocolate and Dog Size
The amount of chocolate consumed and the size of the dog are two key factors that determine how sick a dog will become from chocolate toxicity. This is because the two main chemicals in chocolate that cause toxicity are theobromine and caffeine, which dogs cannot metabolize well.
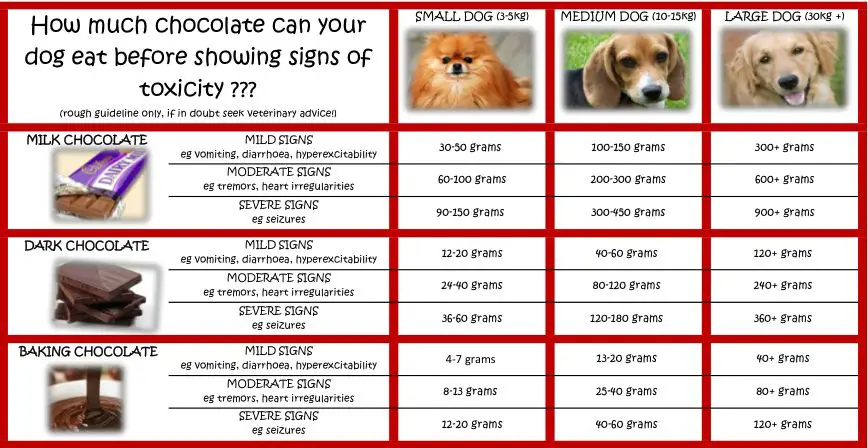
In general, the smaller the dog, the less chocolate it takes to make them ill. According to the VCA Animal Hospitals, for every 1 pound of body weight, it takes approximately 20 mg of theobromine to produce signs of toxicity in dogs. So a 5 pound dog would only need to consume around 100 mg of theobromine to become ill.
Milk chocolate contains around 44-58 mg of theobromine per ounce, while baker’s chocolate contains a whopping 450 mg per ounce. So while it may take 8 ounces of milk chocolate to make a 50 pound dog sick, only 1 ounce of baking chocolate can cause illness.
It’s important to note that every dog is different, so these numbers serve as general guidelines. Consult a veterinarian if you suspect chocolate poisoning, as they can provide a more accurate prognosis based on the specific chocolate consumed and your dog’s weight.
Signs of Chocolate Poisoning
Some common signs that a dog has ingested a toxic amount of chocolate include:
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Increased thirst
- Increased urination
- Restlessness
- Hyperactivity
- Rapid breathing
- Muscle tremors
- Seizures
The onset of signs is variable and depends on the amount and type of chocolate ingested. Mild signs like vomiting and diarrhea may start within 6 hours of ingestion. More severe signs like seizures usually develop within 12-24 hours. Dark chocolate is more dangerous than milk chocolate.
According to VCA Animal Hospitals, in severe cases of chocolate toxicity, dogs can develop muscle tremors, seizures, and even heart failure.
Diagnosing Chocolate Toxicity
If a dog shows any signs of chocolate toxicity, the owner should contact a veterinarian immediately. The vet will begin by taking the dog’s medical history, including details about the type and amount of chocolate ingested and when it happened. They will also perform a physical examination, looking for symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, increased heart rate and body temperature.
There are some specific tests vets can run to check for chocolate toxicity:
- Blood tests – These check for increased levels of theobromine and electrolyte imbalances caused by vomiting and diarrhea.
- Urinalysis – Checks for presence of theobromine and signs of kidney damage.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – Looks for heart arrhythmias and racing heartbeat.
Based on the dog’s symptoms, medical history and test results, vets can determine whether chocolate poisoning is the cause and how severe it may be. The earlier chocolate toxicity is caught and treated, the better the prognosis for the dog.

Sources:
https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/chocolate-poisoning-in-dogs
https://www.merckvetmanual.com/toxicology/food-hazards/chocolate-toxicosis-in-animals
Treating Chocolate Toxicity
The main treatments for chocolate toxicity in dogs aim to limit absorption and remove the toxins from the body. According to UC Davis, the primary treatments include:
- Inducing vomiting if the chocolate was ingested within the last 2 hours
- Administering activated charcoal to absorb toxins in the GI tract
- Starting IV fluids to help flush out toxins and maintain hydration
- Monitoring heart rate and rhythm for arrhythmias
Vets may also give medications like apomorphine to induce vomiting or atropine to manage arrhythmias. In severe cases, dialysis may be needed to filter toxins from the blood. The key is starting decontamination as soon as possible after ingestion before toxins can be absorbed.
Can Chocolate Cause Kidney Failure?
Yes, ingesting chocolate can potentially cause kidney failure in dogs. Chocolate contains a compound called theobromine, which is toxic to dogs. When a dog eats chocolate, the theobromine is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the kidneys.
In the kidneys, theobromine causes vasodilation and diuresis, which increases blood flow to the kidneys and urine production. This can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Theobromine is also directly toxic to kidney tubule cells and can cause acute kidney injury.
Signs of kidney failure from chocolate toxicity include increased thirst, increased urination, vomiting, diarrhea, tremors, seizures, and lethargy. Kidney failure is more likely to occur if a dog eats a large amount of chocolate, especially dark or baking chocolate, which is more concentrated in theobromine.

Kidney failure from chocolate ingestion depends on the amount eaten and timing of treatment. With prompt veterinary treatment including fluids, the prognosis for kidney recovery is often good. However, permanent kidney damage or even death can occur if large amounts were ingested or treatment was delayed.
In summary, chocolate toxicity can potentially lead to acute kidney failure in dogs, but the prognosis depends largely on the amount ingested and how quickly treatment is provided. Preventing access to chocolate is key to avoiding this serious complication.
Prognosis for Dogs with Chocolate Toxicity
The prognosis for dogs who have ingested chocolate depends on several factors, including the amount and type of chocolate eaten, the size of the dog, and how quickly treatment is obtained. According to the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine, the prognosis is good for dogs that have ingested small amounts of chocolate and show mild clinical signs1. However, the prognosis is often poor for cases where a large amount of chocolate was ingested, the dog is very small, or there is a delay in treatment.
With prompt veterinary treatment including decontamination, supportive care, and monitoring, many dogs recover fully from chocolate toxicity. Studies show that most dogs who receive treatment within 4-6 hours after ingesting chocolate have a good prognosis2. The earlier treatment can be started, the better the outcome.
Dogs who have eaten extremely large amounts of chocolate may require hospitalization with intravenous fluids and medication to control heart arrhythmias and seizures. With aggressive treatment, studies indicate over 95% of dogs survive chocolate poisoning3. However, in severe cases, chocolate toxicity can occasionally lead to acute kidney failure or even death if untreated. Monitoring kidney values for several days following chocolate ingestion is important.
Overall, prompt veterinary treatment leads to full recovery in most cases of dogs ingesting chocolate. However, prevention is key, as the longer chocolate toxicity goes untreated, the poorer the prognosis. Dog owners should never hesitate to seek veterinary care immediately if they suspect their dog has eaten chocolate.
Preventing Chocolate Toxicity
The best way to prevent chocolate toxicity in dogs is to keep all chocolate out of their reach. Here are some tips to help keep chocolate away from dogs:
- Store chocolate candies, baking chocolate, and cocoa powder up high or in cabinets dogs cannot access.
- Never leave chocolate unattended on low tables or countertops.
- Be vigilant about picking up any dropped chocolate chips or candy wrappers.
- Teach children not to share or give any chocolate foods to dogs.
- Avoid using chocolate flavored toothpaste or other products that dogs could potentially ingest.
- When baking or cooking with chocolate, keep dogs out of the kitchen.
- Securely lid trash cans containing chocolate food waste.
- Pick up after picnics or parties where chocolate was served.
- Monitor gift baskets and holiday items containing chocolate.
- Read ingredient labels to avoid buying treats containing chocolate for your dog.

Diligence and care around all sources of chocolate will help keep this toxic food out of reach and prevent accidental poisoning in dogs.
Conclusion
In summary, chocolate toxicity is a real danger to dogs. Chocolate contains theobromine and caffeine, which are toxic to dogs. The amount of chocolate ingested and the size of the dog determine the severity of poisoning. Signs of chocolate toxicity include vomiting, diarrhea, hyperactivity, abnormal heart rhythm, seizures, and in severe cases, coma or death. Kidney failure can occur if a large amount of chocolate is ingested.
The amount and type of chocolate determines how quickly treatment needs to start. Mild cases can be treated at home by inducing vomiting and administering charcoal. Severe cases require hospitalization for aggressive treatment like IV fluids and medication. Preventing access to chocolate is key, as the longer it is in a dog’s system, the higher the toxicity.
While not every ingestion leads to extreme complications like kidney failure, chocolate should always be kept far away from dogs. Any amount has the potential to cause toxicity and prompt veterinary care. Knowing the signs of chocolate poisoning and acting quickly can help avoid lasting damage.
