Introduction
Allergies are a common health condition in dogs characterized by an overreaction of the immune system to ordinarily harmless substances like pollen, dust mites, certain foods, insect stings, and more. An allergen triggers an immune response that leads to itchy skin, digestive issues, breathing problems, and other symptoms. This article aims to examine whether canine allergies tend to worsen as dogs age.
Types of Allergies
Canine allergies are typically divided into three main categories: flea allergy dermatitis, food allergies, and environmental allergies.
Flea allergy dermatitis is a common allergy in dogs caused by an allergic reaction to flea bites and saliva. Affected dogs are extremely sensitive to even a single flea bite, which leads to severe itching, redness, hair loss, and hot spots on the skin. This allergy is often seasonal, worsening during warmer months when fleas are most active.
Food allergies occur when a dog’s immune system overreacts to a particular ingredient in their food. Common food allergens for dogs include beef, dairy, chicken, eggs, soy, wheat, and corn. Symptoms of food allergies include gastrointestinal issues like vomiting and diarrhea as well as skin conditions like itchy rashes and ear infections.
Environmental allergies, also called atopic dermatitis or inhalant allergies, are caused by allergens in the air, such as dust mites, pollen, and mold spores. Dogs with environmental allergies tend to lick and scratch their skin constantly, leading to skin damage and secondary infections. These allergies are often seasonal but can persist year-round in some climates.
Symptoms
Allergies in dogs can cause a wide variety of symptoms. Some of the most common allergy symptoms in dogs include:
Itchy skin
One of the classic signs of allergies in dogs is extreme itchiness of the skin. Dogs with allergies may scratch, lick, or chew at their skin constantly in an effort to relieve the irritation.
Ear infections
Allergies can also cause inflammation and infection of a dog’s ears. Dogs with ear allergies will often shake their head and scratch at their ears attempting to relieve the discomfort.
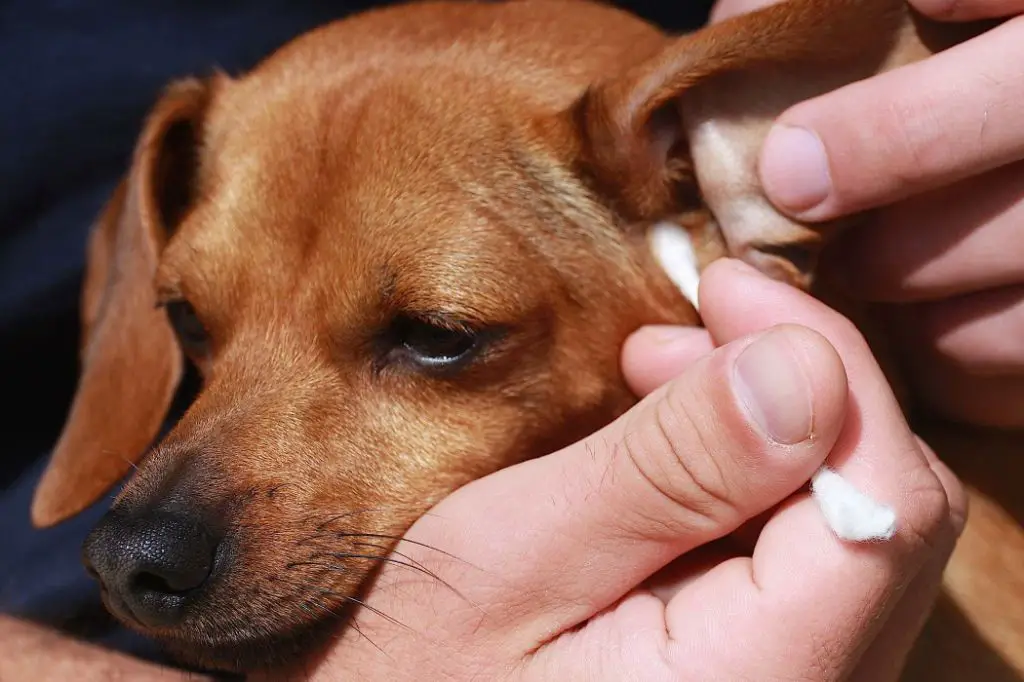

Paw chewing
Some dogs may lick or chew at their paws when suffering from allergies. This is because allergens like pollen can collect on the paws when outside, causing itchiness and irritation.
Digestive issues
Allergies can sometimes cause stomach and digestive problems in dogs as well, including vomiting, diarrhea, and excessive gas.
Causes
The root cause of allergies in dogs is an overactive immune system that mistakenly identifies harmless substances as threats. The immune system produces antibodies called immunoglobulin E (IgE) that bind to the allergen and trigger the release of chemicals like histamine that lead to inflammation and allergy symptoms.
Genetics play a role as well. Some dog breeds like retrievers, terriers, and poodles are more prone to developing allergies due to their genetics. The heritability of canine atopy is around 0.47, meaning almost half the risk is inherited.
Environmental factors also contribute. Allergens from food, insects, plants, or other substances that dogs inhale or ingest can trigger an overzealous immune reaction in susceptible pups. Things like dust mites, mold spores, pollen, and certain proteins in food are common environmental allergens.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing allergies in dogs requires visits with a veterinarian to rule out other conditions and identify the allergen through testing. The main diagnostic methods include:
Veterinarian Examination
The veterinarian will perform a complete physical exam and take the dog’s full medical history. They will look for clinical signs characteristic of allergies, such as itchy skin, recurring ear infections, and hair loss. The exam helps rule out other conditions like skin infections or hormone disorders.
Elimination Diet Trials
The veterinarian may recommend feeding the dog a hypoallergenic dog food for 8-12 weeks. If the symptoms resolve, it indicates a food allergy. Then different proteins can be reintroduced to identify the problematic ingredients.
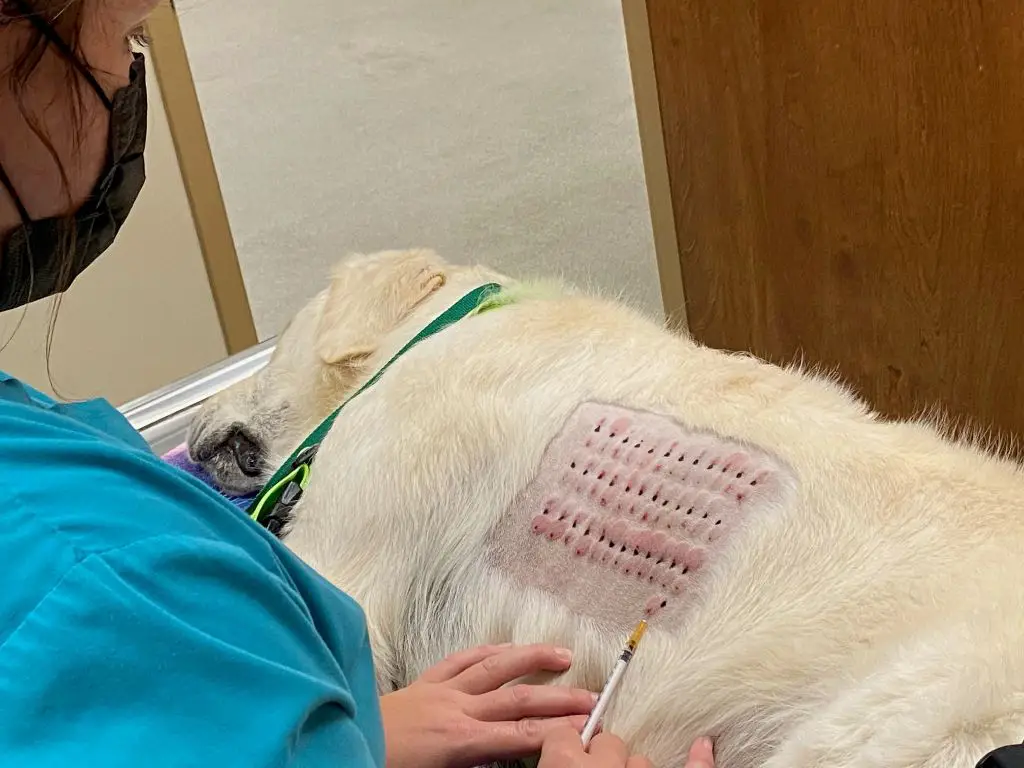
Intradermal Skin Tests
Skin testing identifies allergies to specific environmental allergens. Small amounts of suspected allergens are injected into the dog’s skin and any reaction indicates an allergy. Then allergen-specific immunotherapy injections can be prescribed.
Age of Onset
Allergies can appear at any stage of a dog’s life, but often the first symptoms are seen when a dog is between 6 months and 3 years old. This age range is when dogs are most commonly exposed to new antigens that can trigger allergic reactions. However, allergies may develop later in life as well. Some dogs don’t develop allergies until they are seniors, while others have symptoms present from birth or that appear when they are puppies. So while there are typical age ranges, allergies truly can arise at any point in a dog’s life.
Do Allergies Worsen with Age?
Yes, allergies often do worsen as dogs get older. This is due to several factors related to the aging process.
As dogs age, their immune systems often become dysfunctional and less effective at fighting off allergens. The natural defenses against allergic reactions weaken over time. This means the body mounts a stronger inflammatory response when exposed to allergens later in life.
Additionally, dogs are exposed to more allergens over their lifetime. Each year brings new exposure to potential allergens that may sensitize the immune system. The longer a dog lives, the more likely they are to develop hypersensitivities to various allergens.
With prolonged exposure over many years, dogs tend to develop more exaggerated responses to allergens they were previously only mildly sensitive to. Their bodies’ reactions intensify over time.
In summary, aging dogs see their allergies worsen due to cumulative exposure and declining immune function. Their bodies become less equipped to handle allergens they once tolerated earlier in life. Taking steps to manage allergies is crucial for aging dogs.
Managing Allergies
There are several ways to help manage allergies in dogs as they age:
Avoidance of Allergens
Since allergies are reactions to allergens in the environment, avoiding exposure to these allergens can help reduce symptoms. This may involve keeping your dog indoors during peak pollen seasons, using high efficiency filters in your home, washing bedding regularly, and avoiding going to areas with irritants like cigarette smoke or perfumes.
Medications
Your veterinarian may prescribe medications like antihistamines, steroids, or immunosuppressants to reduce inflammation and provide relief from allergy symptoms. These medications can be adjusted over time as the allergies progress.
Immunotherapy
Allergy shots or drops containing small amounts of the antigens your dog is allergic to can help desensitize their immune system over time. This immunotherapy may need to be adjusted as your dog ages.
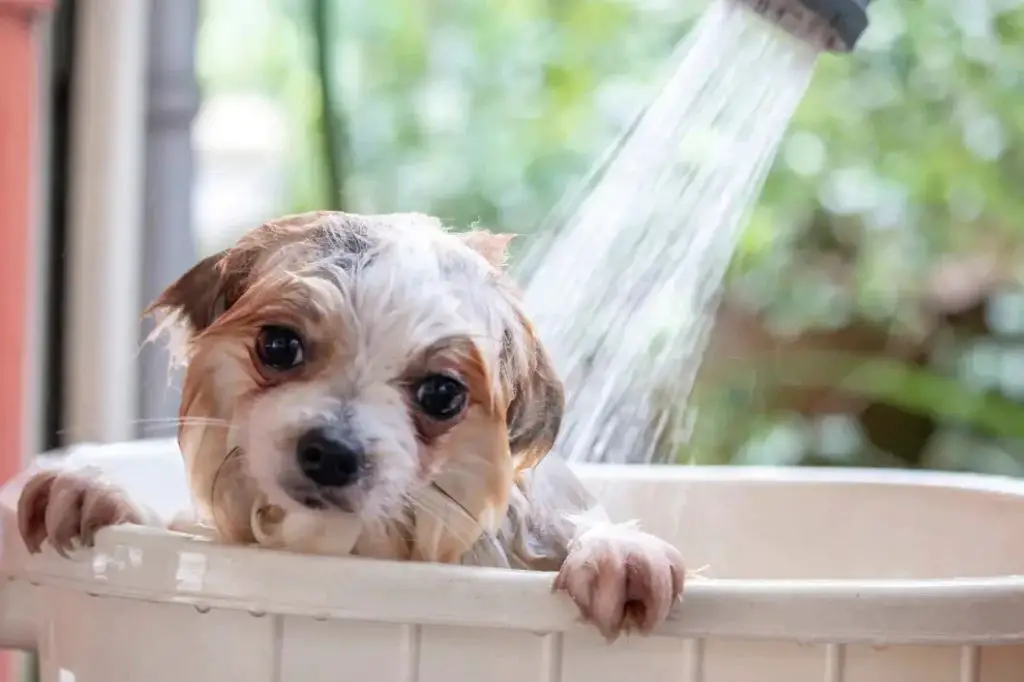
Bathing Regimen
Bathing your dog regularly with a veterinarian-recommended shampoo can help wash off pollen and other allergens and soothe irritated skin. Over time, your veterinarian may recommend trying different shampoos or adjusting the bathing schedule as your dog’s allergies change.

Prognosis
Allergies in dogs are usually a lifelong condition. Once a dog develops allergies, they tend to persist throughout their lifetime. There is no cure for allergies, so they cannot be completely eliminated.
However, with proper management and treatment, allergies can be controlled so they do not significantly impact a dog’s quality of life. While allergies may worsen with age, the symptoms can be managed through medications, dietary changes, and environmental control. This allows dogs with allergies to live happily and comfortably despite their condition.
So while allergies are chronic, they do not mean a poor prognosis if properly diagnosed and treated. With the right care, dogs with allergies can have a good quality of life for years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evidence suggests that allergies in dogs do tend to get worse with age. As dogs grow older, their immune systems may become less effective at protecting against allergens. Additionally, repeated and prolonged exposure over a lifetime can make dogs become sensitized to more environmental allergens. Therefore, allergies often start at a young age but increase in frequency and severity as dogs age.
The good news is that allergies in aging dogs can be effectively managed with medications, immunotherapy, diet changes, and avoiding triggers. While allergies may worsen over time, dogs can live comfortably into their senior years through proper treatment and management. With an accurate diagnosis and veterinary guidance, worsening allergies do not have to mean a poor quality of life for aging dogs.