History of Dog Handling
The bond between humans and dogs dates back over 15,000 years to when early hunter-gatherers began domesticating wolves. Dogs became invaluable partners assisting humans with hunting, providing protection, and herding livestock. Throughout history, dogs continued serving in working roles according to the needs of the time – from war dogs to herding dogs on farms.
Training methods evolved from simply rewarding desired behaviors to more complex techniques. In the past, punishment-based methods using force were common for obedience training. However, as understanding of canine behavior and psychology has improved, reward-based positive reinforcement has become the gold standard for effectively shaping dog behavior while building a strong relationship.
Common Methods of Dog Handling Today
Dog training and handling methods have evolved significantly in recent decades as scientific research has provided new insights into canine behavior and psychology. Today, most experts promote positive reinforcement as the preferred method for training dogs. This involves rewarding desired behaviors and ignoring unwanted behaviors.
Some trainers still use techniques based on negative reinforcement, which applies an unpleasant stimulus until the dog complies. Similarly, punishment involves imparting an unpleasant consequence to stop an undesirable behavior. However, research shows that these methods, sometimes called “dominance-based,” tend to be less effective and potentially harmful.
Positive reinforcement builds a cooperative relationship between handler and dog by making training enjoyable. It focuses on teaching the dog what to do rather than punishing mistakes. Food treats, praise, petting and play can all be used as rewards. Recent studies confirm that reward-based training is more successful at teaching obedience and reducing problem behaviors.
In contrast, dominance and punishment models originated from flawed assumptions about wolf pack hierarchies. Dogs are not wolves, and this outdated view often leads trainers to use confrontation, intimidation and physical corrections. Scientific evidence shows that these techniques are risky, induce stress, and often backfire by increasing a dog’s fear and anxiety.
Today’s science-based handling uses positive reinforcement to build a relationship of mutual trust and teach the dog proper manners. This empowers dogs to willingly cooperate using motivation rather than fear. Reward-based training helps handlers bring out the best in their dogs.
Training Approaches
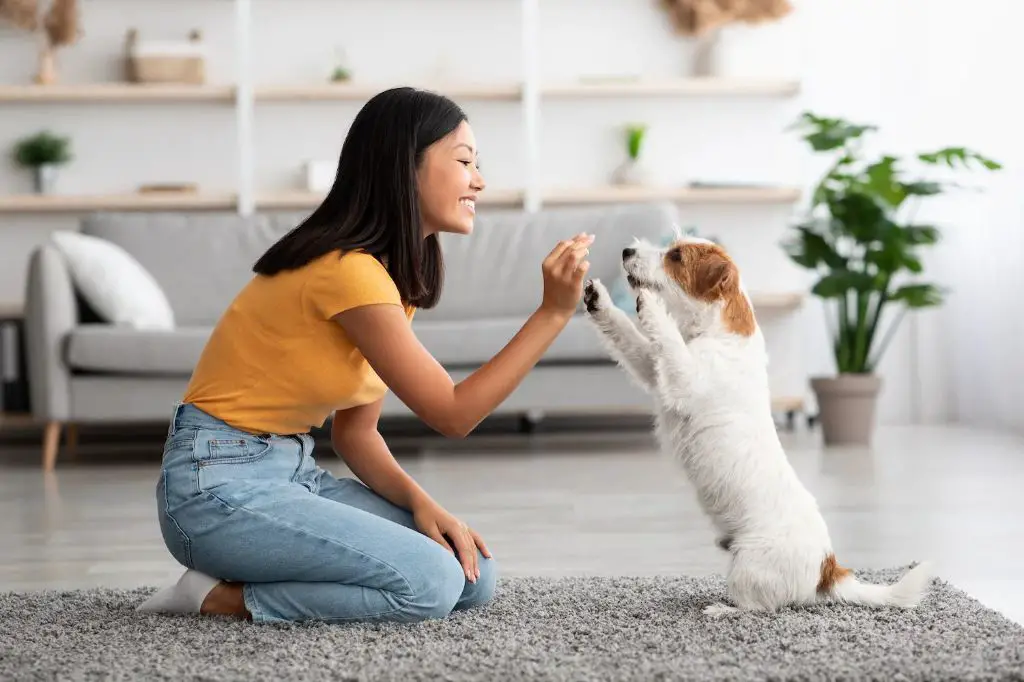

There are several common training methods used today to teach dogs basic obedience and tricks.
Clicker Training: This method relies on conditioning a dog to associate the sound of a “clicker” device with receiving a reward. The clicker precisely marks the desired behavior, allowing the trainer to reward the dog at the exact right time. Clicker training uses positive reinforcement and enables dogs to learn quickly.
Treat Training: Also known as reward-based training, this approach uses food treats to reinforce desired behaviors. The dog gets a treat immediately upon displaying the correct response to a command. Treat training takes advantage of a dog’s natural food drive to motivate learning.
Verbal Commands: Simple spoken words like “sit,” “stay,” or “down” are commonly taught to dogs. Verbal commands allow handlers to communicate instructions and praise to the dog during training. Commands are often paired with other reinforcement like treats.
Hand Signals: Visual hand motions and signals are another way handlers can cue dogs. A point, wave, or open palm can indicate different behaviors for a dog. Hand signals are especially helpful for hearing impaired dogs or in loud environments.
Socialization
Proper socialization is crucial for raising a happy and well-adjusted dog. Puppies have a short window of opportunity, from 3 to 16 weeks old, to be exposed to new environments, people, animals, and experiences. This exposure during the early months helps prevent fearfulness and anxiety later on.

Socialization involves gradually and positively introducing puppies to everyday sights, sounds, smells, and sensations in a controlled way. For example, taking them on car rides, inviting friends over to meet the puppy, letting them hear loud noises like vacuums, and having them walk on different surfaces like tile, grass, and concrete. The goal is to make the puppy confident and comfortable in any situation.
Pet owners should also allow their puppy to interact with other vaccinated, healthy puppies and friendly adult dogs. This teaches them proper social skills and bite inhibition. However, it’s important not to overwhelm the puppy or force interactions if they seem frightened. Socialization requires patience, positive reinforcement, and keeping things low-key.
Preventing under-socialization can help avoid common behavioral issues stemming from fear, reactivity, separation anxiety, and aggression. Puppies that are properly socialized tend to be friendlier, calmer, and more adaptable as adult dogs.
Exercise
Exercise is an extremely important part of caring for a dog. It’s important to provide your dog with enough physical and mental stimulation to prevent problem behaviors from developing due to boredom, frustration or excess energy. The amount of exercise a dog needs varies greatly based on breed and age.
For high-energy breeds like Border Collies, Labrador Retrievers and Jack Russell Terriers, at least 30-60 minutes of vigorous activity per day is recommended. This could include activities like playing fetch, going for runs or hikes, swimming, or playing with other dogs. Interactive toys and training activities also provide mental exercise.
Lower energy breeds like Basset Hounds, Pugs and Cavalier King Charles Spaniels require less intense exercise, but still need multiple short walks per day and play. Senior dogs and puppies should not be over-exercised.
Providing adequate physical and mental stimulation is key to having a well-behaved and relaxed dog. Boredom can lead to destructive behaviors like chewing, digging, excessive barking and aggression. An exercised dog is a happy dog!
Nutrition
Proper nutrition is essential for a dog’s health and wellbeing. Most experts recommend feeding dogs a high-quality commercial dog food that meets nutritional standards established by the Association of American Feed Control Officials. When selecting a commercial diet, look for brands that indicate they have undergone feeding trials. Avoid brands with lots of fillers like corn, wheat, and soy.
Some dog owners opt to prepare homemade diets for their dogs. This allows for more control over ingredients, but it’s important to consult with a veterinary nutritionist to ensure the diet is balanced. Homemade diets take more effort and oversight than commercial dog food.
Supplements can provide nutritional support, but should be used carefully under veterinary supervision. Common supplements for dogs include probiotics for digestive and immune health, fish oil for skin and coat health, and joint supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin for mobility.
Grooming
Grooming is an important part of caring for a dog’s health. Regular grooming keeps a dog’s coat clean, free of mats, and looking its best. Grooming also provides an opportunity to check for any abnormalities on the skin or coat. The main grooming tasks for dog owners are brushing, bathing, nail trimming, and dental care.
Brushing and Bathing
Most dogs benefit from regular brushing to remove loose hair and distribute skin oils. Brushing helps prevent mats and knots from forming in the fur. Dogs with long or thick coats require more frequent brushing than short-haired breeds. Baths can be given as needed, usually every few months, to keep the coat and skin clean. Use a mild dog shampoo and rinse thoroughly after washing.
Nail Trimming
Trimming a dog’s nails regularly prevents the nails from cracking or splitting and keeps them at a comfortable length. Long nails can catch on surfaces and tear. Trimming also keeps the dog from scratching and causing injury if it has overly long nails. Special nail trimmers designed for dogs should be used.
Dental Care
Regular dental care keeps a dog’s teeth and gums healthy. Brushing the teeth prevents plaque buildup and tooth decay. Dog toothbrushes and toothpastes are available for home dental care. Chew toys and treats can also help clean teeth. Professional cleanings by a vet may be needed periodically to fully remove tartar from the teeth.
Veterinary Care
Veterinary care is an essential part of properly handling a dog. Most vets recommend bringing dogs in for annual exams to check their overall health and administer necessary vaccines. During annual exams, vets will do a physical checkup, take the dog’s temperature and weight, check their coat, ears, eyes, heart, lungs, skin, joints, and more. Bloodwork may be recommended to check for any potential issues.
Vaccines help prevent contagious and potentially fatal diseases like distemper, parvo, and rabies. Core vaccines that all dogs should receive include distemper, adenovirus, parvovirus, and rabies. Non-core vaccines may also be recommended based on the dog’s lifestyle and risks. Keeping up with a vaccine schedule is key to preventative care.
Dog owners should monitor their pet’s behavior and health in between vet visits. Changes in appetite, energy level, bathroom habits, mood, or physical condition could indicate illness. Recognizing symptoms early allows veterinary treatment to begin sooner for the best outcome. Being alert to any coughing, limping, growths, rashes, or other concerning signs helps owners get their dogs the care they need right away.
Creating a Safe Environment
To keep your dog safe at home, it’s important to properly dog-proof your house and yard. Make sure there are no small objects lying around that your dog could swallow and choke on. Keep medications, toxic plants, chemicals, and cleaning supplies securely out of reach. Secure loose wires, hide exposed electrical cords, and place barriers around unsafe areas like staircases.
Your dog should always wear a collar with proper identification, including your contact information and any other important tags. Consider microchipping your dog as another form of identification. Update your contact info with the microchip company if you move or change phone numbers.
Be prepared for emergencies with a pet first aid kit and information on your local emergency vet clinics. Know the signs of common pet emergencies like bloat, heat stroke, poisoning, injuries, and allergic reactions. Keep your vet’s number handy and have a plan to transport your dog safely if an emergency arises.
Meeting a Dog’s Emotional Needs

Dogs have emotional needs just like humans do. As their caretakers, it’s important that we provide for these needs to ensure our dogs live happy, fulfilled lives.
One of the most important emotional needs for dogs is companionship. Dogs are pack animals and crave being around their family. Make sure to spend plenty of quality time interacting with and playing with your dog each day. Going for walks together is a great way to bond.
Positive interactions are also key. Use rewards-based training approaches focused on trust and mutual understanding. Avoid punishment or scolding, which can damage the human-animal bond. Give your dog plenty of affection and make sure they know they are a beloved member of the family.
Providing a sense of security and consistency is also vital for a dog’s emotional wellbeing. Establish a daily routine your dog can rely on. Prepare comfortable resting areas in quiet rooms of your home. Minimize disruptions, loud noises or chaos that could create stress. Help your dog feel safe, cared for, and secure in their environment.
By fulfilling these basic emotional needs – companionship, positive interactions, security and consistency – you can ensure your dog lives a happy, low-stress life and develops a strong mutual bond with you built on trust and care.