Introduction to False Pregnancy in Dogs
False pregnancy, also known as pseudopregnancy, is a condition that occurs after a female dog goes through estrus or experiences an estrus-like cycle without actually being pregnant. It is characterized by behavioral, physical, and hormonal changes that mimic normal pregnancy even though conception did not occur (Root, 2018).
Common symptoms of false pregnancy in dogs include nesting behavior, mothering inanimate objects, lethargy, enlarged mammary glands, and milk production. The exact prevalence of false pregnancy in dogs is unknown, but some studies estimate it affects up to 50-75% of intact female dogs to some degree (Root, 2018; Juniper Publishers, 2019).
Causes of False Pregnancy
False pregnancy in dogs occurs due to hormonal changes after an estrus (heat) cycle combined with psychological factors. After a female dog goes into heat, their progesterone levels remain elevated for up to two months to prepare the body for pregnancy and nursing even if conception does not occur. These hormonal changes alone can trigger many of the symptoms of pregnancy. In addition, some female dogs may experience psychological longing for puppies that contributes to them exhibiting mothering behaviors.
According to the VCA Hospitals, the heightened progesterone levels “send signals to the body to stimulate false labor and mammary gland development.” After approximately two months, progesterone levels decline, triggering the physical and behavioral changes associated with false pregnancy.
Both the hormonal fluctuations and a female dog’s natural mothering instincts can contribute to false pregnancy symptoms such as nesting, mothering toys, and milk production. However, the root cause remains the hormonal changes triggered by an unbred heat cycle.
Common Symptoms
The most common symptom of false pregnancy in dogs is swollen mammary glands. The hormones progesterone and prolactin cause the mammary glands to swell and may even produce milk. The dog may even try to relieve the pressure in their mammary glands by self-nursing and making motions similar to normal nursing. The mammary glands can remain swollen for several weeks to months after the false pregnancy symptoms begin.
Dogs experiencing false pregnancy also commonly exhibit nesting behaviors like gathering toys, blankets, or other objects to create a comfortable, safe space. They become highly protective and affectionate towards their “nest”.
Along with nesting behaviors, dogs with false pregnancy often begin mothering toys or other inanimate objects. They may carry the toys around gently in their mouth and treat them like real puppies by allowing the toys to nurse. Some dogs even growl or act aggressive if their ‘puppies’ are taken away.
Differential Diagnosis
To correctly diagnose pseudopregnancy, veterinarians must first rule out a true pregnancy using diagnostic testing. An ultrasound or X-ray can determine whether there are fetuses present or not [1]. Bloodwork may also indicate elevated progesterone levels during early pregnancy.
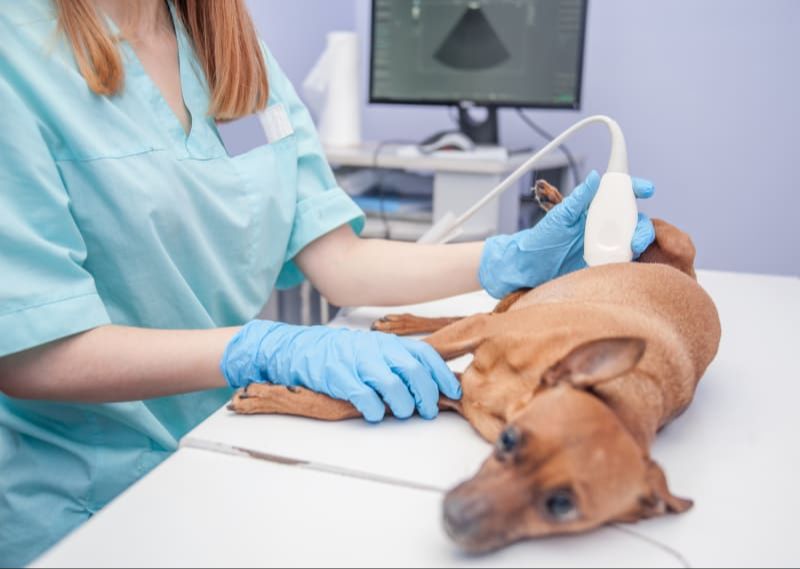

Other conditions that may initially look similar to pseudopregnancy must also be considered in the differential diagnosis. Mastitis or mammary gland infection can cause swelling and milk production. Pyometra, a uterine infection, can also sometimes mimic the signs of a false pregnancy. Ultimately, diagnostic testing is required to distinguish pseudopregnancy from these other conditions.
Physical Exam Findings
The veterinarian will perform a full physical examination on the dog to check for signs of false pregnancy. Some of the key things the vet will look for include:
Enlarged mammary glands – One of the most obvious signs of false pregnancy is enlarged or swollen mammary glands. The hormones prolactin and progesterone cause the mammary glands to enlarge and become capable of producing milk, even if the dog is not actually pregnant [1].
Abdominal palpation – The vet will gently palpate the dog’s abdomen to feel for any abnormalities. In a false pregnancy, the abdomen may feel enlarged or firmer than normal. However, there will be no fetuses present upon palpation [2].
Diagnostic Tests
There are a few diagnostic tests vets can use to confirm false pregnancy in dogs:
Progesterone Testing – Measuring progesterone levels can help diagnose false pregnancy. Progesterone levels will be elevated at the start of a true pregnancy, while dogs with false pregnancy typically have normal progesterone levels (VCAA).
Ultrasound – An ultrasound allows vets to visualize the uterus and look for signs of pregnancy, such as placental attachments or fetuses. If no evidence of pregnancy is seen on ultrasound in a dog exhibiting pregnancy symptoms, it supports a diagnosis of false pregnancy (PetMD).
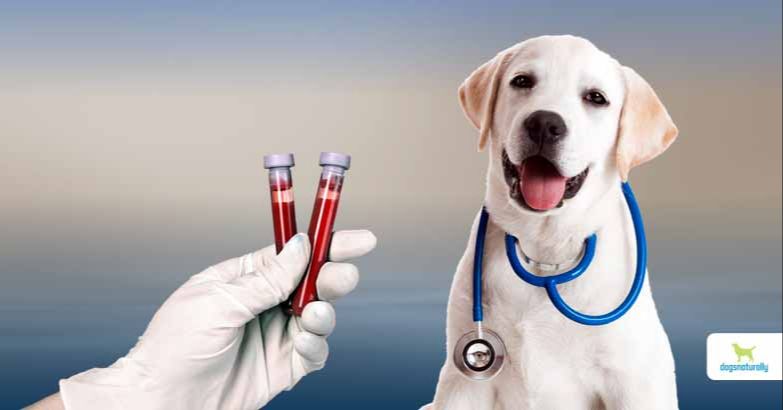

Blood Counts – Dogs with a true pregnancy will have an elevated white blood cell count. Normal blood work in a symptomatic dog makes false pregnancy more likely (Merck Veterinary Manual).
Treatment
There are a few options for treating false pregnancy in dogs:
One option is to simply allow the condition to run its course. With supportive care and patience, symptoms will usually resolve on their own within 2-3 weeks. However, this may not be ideal if symptoms are severe.
Medications can help shorten duration and relieve symptoms. Drugs like cabergoline, bromocriptine [1], and metergoline can block prolactin and shorten episodes to around 5 days [2]. Tranquilizers may ease anxiety and discomfort. Diuretics can reduce fluid buildup and milk production.
Spaying is a permanent solution that prevents recurrence, since false pregnancies only happen in intact females. However, this invasive surgery carries risks and may not be the best option for all dogs.
Caring for a Dog with False Pregnancy
If your dog is experiencing a false pregnancy, there are some things you can do at home to help care for her:

Limit mammary gland stimulation. Dogs experiencing false pregnancy may become increasingly protective of their milk supply. Do not encourage nursing behaviors by allowing access to stuffed toys or other objects she may try to “nurse.” Limiting access can help reduce this behavior over time.
Provide adequate outlets for mothering. Your dog may try to mother or nurture objects around the home. Providing a warm blanket or safe chew toy can give her an appropriate outlet. Supervise closely to ensure her mothering behaviors do not become obsessive.
Gently discourage excessive licking of nipples to avoid irritation. If the mammary glands become inflamed or infected, speak to your veterinarian about medication to reduce swelling or prevent infection.
Offer extra love and affection to help her feel secure. The hormones related to false pregnancy can cause behavioral changes. Remaining patient and keeping her routine consistent can help.
Monitor for signs of depression or lethargy. Some dogs may experience shifts in mood. If these signs persist beyond a few days, consult your veterinarian.
Schedule a vet visit if symptoms worsen or do not resolve within 2-3 weeks. In most cases rest, patience, and TLC at home can help a dog through a false pregnancy. But veterinary intervention may sometimes be needed.
Prevention
There are a few ways to help prevent false pregnancy in dogs:
Spaying your dog is the most effective way to prevent recurring false pregnancies. Spaying refers to ovariohysterectomy, which is the surgical removal of the ovaries and uterus. This eliminates the source of progesterone that causes false pregnancy symptoms. Most vets recommend spaying dogs around 6 months of age, before the first heat cycle, to prevent false pregnancies from developing.
Limiting psychological triggers can also help reduce episodes of false pregnancy. Since false pregnancies are often triggered by the hormones related to a heat cycle, keeping your dog away from intact males during her heat can help. Reducing physical contact with her mammary glands and avoiding overly attentive behavior from owners can also help discourage mothering behaviors. Providing diversions and exercise during times she normally would experience false pregnancy symptoms may lessen the intensity as well.
For intact dogs who are being bred, allowing them to finish nursing and wean a full litter of puppies can sometimes prevent subsequent false pregnancies. However, the only sure way to prevent recurrence is ovariohysterectomy once the dog is done being bred.
Source: https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/false-pregnancy-or-pseudopregnancy-in-dogs
Prognosis
The prognosis for false pregnancy in dogs is generally excellent with proper care. In most cases, the condition will resolve on its own within 2-3 weeks without any specific treatment (PetMD). Dogs experiencing a phantom pregnancy will return to normal behavioral and physical health once hormone levels stabilize (VC Hospitals).
It’s important to provide extra love and attention during this time, but not overstimulate or encourage the false pregnancy behaviors. As long as the owner continues to meet the dog’s needs for exercise, stimulation and affection, the false pregnancy symptoms should subside quickly. Most dogs will make a full recovery within a few weeks (WebMD).
In rare cases when the false pregnancy symptoms persist longer than 4-5 weeks, veterinary intervention may be needed. However, the prognosis remains good with proper treatment. With medication and environmental management, the vast majority of dogs will overcome a false pregnancy and not experience complications or impacts to future fertility.