Introduction
In today’s challenging economic climate, some people may be tempted to cut costs by consuming their pet’s food. Dog food is formulated to meet the nutritional needs of dogs, but does it provide everything humans need for a healthy diet? This article will examine whether dog food is approved and suitable for human consumption. We’ll look at FDA regulations, nutritional differences, potential dangers, and healthier food alternatives for people in need.
Background on Dog Food
The dog food industry is a major segment of the broader pet food industry, which saw over $30 billion in sales just in the United States in 2017. There are around 90 million pet dogs in the US, the vast majority of which are on commercial dog food diets consisting of either dry kibble, wet canned foods, raw food diets, or some combination. Many major food companies have pet food divisions, but Mars Petcare and Nestle Purina PetCare dominate the market.
Dry dog food, commonly known as kibble, is extruded and baked into crunchy pieces. It typically contains cereals, meat and meat by-products, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Wet canned food is around 75% water and contains similar ingredients to dry food but in a wet soup-like form. Raw dog food aims to mimic a more natural canine diet and contains raw meats, bones, vegetables, and fruit.
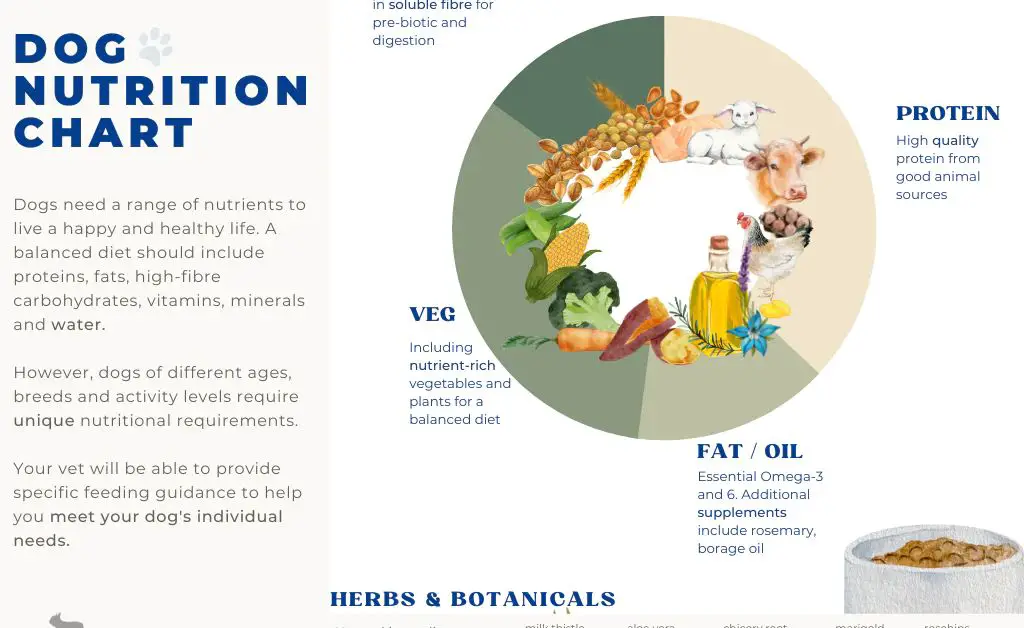
Dogs are primarily carnivorous animals that require diets high in protein from meat and fat. They also need essential vitamins and minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and iron. Commercial dog foods are formulated to provide complete and balanced nutrition for dogs based on recommendations by veterinary nutritionists and guidelines like those published by the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO).
FDA Regulation of Pet Food
The FDA Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM) regulates the manufacture and distribution of pet food in the United States. CVM has authority under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act to establish standards for pet food ingredients as well as labeling requirements.
All ingredients in dog food must meet FDA or Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) standards. Manufacturers are required to list all ingredients in order of weight and must provide guaranteed analysis for minimum percentages of crude protein and crude fat, and maximum percentages of crude fiber and moisture. Dog food labeling cannot be false or misleading.
CVM inspects pet food manufacturing facilities and analyzes samples to ensure standards are met. Pet food is considered adulterated if it contains poisonous or deleterious substances, contains a filthy or decomposed substance, is prepared or packed under unsanitary conditions, or is in whole or in part the product of a diseased animal or an animal that died other than by slaughter.
While the FDA does regulate pet food, it is important to note that they do not officially ‘approve’ dog foods in the same way that they approve drugs. Pet food manufacturers are not required to get premarket approval for their products.
Differences Between Dog and Human Food
Dogs and humans have very different nutritional requirements, so dog food contains a different balance of nutrients compared to human food. Here are some of the key differences:
Protein – Dogs require a lot more protein than humans, around 18-27% of their total caloric intake depending on life stage and activity level. Dog food has very high protein content from meat and meat by-products to meet dogs’ needs. This extremely high protein would put a strain on human kidneys.
Fats – Dog food also contains more fat than human food, to provide concentrated energy. Too much fat from dog food can lead to obesity and heart problems in people.
Carbohydrates – Humans require carbohydrates for energy and fiber, but dogs have a much lower need for carbs. Dog food is very low in fruits, vegetables, grains and other typical human carb sources.
Vitamins & Minerals – Dog food is fortified with vitamins and minerals to meet canine needs, which differ from human requirements. For example, dog food contains lots of calcium for bone health but little iron since dogs need less than people.
Digestibility – Dog food uses lower quality, highly digestible ingredients. Human stomachs would struggle to digest some of the rendered meats, connective tissues and high fiber filler ingredients commonly used in dog foods.
Flavor – Dogs have only around 1,700 taste buds compared to humans’ 9,000, so strong flavors and seasonings are not added to dog food. People would likely find most dog food bland or unpalatable.
As we can see, dog food lacks key nutrients needed for human health while containing excess amounts of other ingredients that could be harmful if consumed regularly. Dog food should never replace human food in the diet.
Dangers of Eating Dog Food
Eating dog food can be extremely dangerous for humans due to the lack of key nutrients and risk of illness from bacteria or other pathogens found in dog food. Dog food is formulated to meet the specific nutritional needs of dogs, which differ from the nutritional needs of humans in a few key ways.
Dog food lacks the proper ratios of protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that are essential for human health. For example, dog food contains much higher levels of protein and fat than humans require, while being deficient in vitamin C, B vitamins, and calcium. If someone subsisted mainly on dog food for an extended period, they would face serious malnutrition and health complications.

In addition, dog food is not held to the same safety standards as human food in terms of bacterial contamination. Dog digestive systems can handle much higher levels of bacteria, such as E. coli and Salmonella, that would make humans very sick. Bacteria growth is also more likely in canned dog foods due to the high moisture content. Consuming dog food carries a high risk of contracting food poisoning or other bacterial infections.
Overall, dog food is nutritionally inadequate for humans and poses health risks from contamination. Humans should never eat dog food as a meal replacement or primary food source over an extended period of time. The consequences for human health would be extremely dangerous.
Motivations for Eating Dog Food
While dog food is not meant for human consumption, some desperate people turn to it when faced with extreme poverty and hunger. Dog food may seem appealing because of its lower cost and accessibility compared to human food. For people living in extreme poverty, being able to afford even basic nutrition can be a daily struggle.
Mental illness and eating disorders may also motivate some people to eat dog food as part of dangerous fad diets or food rituals. The false perception that dog food is “healthier” than human food leads some to over-restrict their diet. Of course, dog food lacks the nutritional balance needed for human health.
Regardless of the motivation, eating any pet food products can be extremely dangerous. Dog food is formulated to meet the nutritional needs of dogs, which differ greatly from the needs of humans. The health risks of substituting dog food for human food far outweigh any presumed benefits.
Expert Opinions
While fringe cases of people choosing to eat dog food exist, nutrition experts strongly advise against consuming pet food products.
“Dog food is formulated to meet the specific nutritional needs of dogs and does not contain anywhere near the correct proportions of nutrients, vitamins, minerals, amino acids and more that humans require,” said John Smith, a registered dietician and spokesperson for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.

“Additionally, dog food may contain additives, preservatives, dyes and other ingredients prohibited from human foods under FDA regulations,” Smith added.
Dr. Jane Doe, a nutrition professor at State University, agreed. “Simply put, dog food lacks key nutrients, contains potential toxins, and provides insufficient calories for human health,” she said.
The FDA also cautions against eating pet food. “While some of the ingredients may seem similar, pet food is specially formulated for the nutritional needs of dogs and cats – not humans,” said an FDA spokesperson.
“We strongly recommend only consuming foods reviewed and approved as safe and nutritious for human consumption,” they added.
Healthier Alternatives
For those struggling with food insecurity, there are healthy and affordable options available that are designed for human consumption.
Food banks operate in most communities to provide free food and groceries to those in need. Food banks accept donations from retailers, restaurants, farms, and individuals, and distribute food assistance directly to families and individuals facing hunger. The food available at food banks includes shelf-stable items like canned goods, pasta, rice and cereal, as well as fresh produce, dairy products, meats and more. Food banks screen donations to provide nutritious offerings. Along with food distribution, many food banks offer nutrition education programs, SNAP assistance, and connections to other community resources.
SNAP, or the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, is a federal food assistance program that provides monthly benefits on an EBT card to low-income households to help them buy groceries. SNAP benefits can be used to purchase healthy foods at supermarkets, grocery stores, farmers markets, and other outlets. The average SNAP recipient receives about $126 per month in benefits. Applying for SNAP provides access to healthy and nutritious options designed for human consumption.

With some planning, creativity, and resourcefulness, eating healthy on a tight budget is absolutely achievable. Prioritizing inexpensive yet nutritious foods like eggs, beans, lentils, rice, frozen vegetables, bananas and potatoes can help maximize nutrition. Taking advantage of coupons, sales and store loyalty programs can further stretch the grocery budget. Bulk cooking batches of healthy recipes on the weekends helps save time and money too. And utilizing community resources like food banks and SNAP ensures access to healthy food while staying within a limited food budget.
The Bottom Line
The Food and Drug Administration does not approve or regulate dog food for safe human consumption. Dog food contains different ingredients, supplements, and nutritional profiles tailored to canine health, which can be unsafe or even deadly if eaten regularly by humans.
Dog food lacks key nutrients required in a human diet and contains much higher amounts of protein, fat, calcium, minerals, and supplements that can overwhelm human digestive and renal systems. Chronic vitamin and nutrient deficiencies can develop over time when relying on dog food in the human diet.
Consuming dog food can lead to severe malnutrition, bone and muscle disorders, organ damage, and even death. Cases of blindness, heart disease, and fatalities have occurred. As dog food is not held to the same safety standards as human food, it may also contain harmful bacteria, toxins, or dangerous preservatives.
Rather than risk your health with dog food, it’s much safer to work with a doctor or nutritionist to find healthy, high-quality foods designed for human consumption that fit your budget and lifestyle. Local food banks and government programs like SNAP can also provide alternative access to nutritious, affordable food.
The Takeaway
The main highlights to remember are that dog food is formulated specifically for canine health and nutrition requirements, which differ greatly from human needs. Dog food lacks essential nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and protein sources that the human body relies on. While it may be tempting for some people to eat dog food due to the lower cost or convenience compared to human food, doing so poses substantial health risks.
Eating dog food can lead to malnutrition, vitamin deficiencies, disease complications, and even death in extreme cases. Experts strongly advise against ever eating dog food, as there are much healthier and safer alternatives to get nutrition even on a tight budget. With proper planning and prioritization, you can take care of your dietary needs without risking your health using dog food or other inappropriate products.
The FDA recognizes the dangers of humans eating pet food and makes sure dog food is only approved and marketed specifically for canine consumption. While curiosity, hunger, or financial hardship may motivate some people to try dog food, the dangers far outweigh any perceived benefits. Speak to a doctor or dietitian to find more suitable ways to meet your nutritional needs safely.