Introduction
Homemade dog food has become increasingly popular over the past decade. An increasing number of dog owners are rejecting kibble in favor of preparing food for their dogs in their own kitchens. Advocates of homemade dog food claim it is healthier, more natural, and more customizable to a dog’s nutritional needs. While the homemade dog food trend may have benefits, it also requires work, planning, and care to ensure meals are balanced and safe. This article provides an overview of the homemade dog food trend, including the potential pros and cons, key considerations, and guidance for owners who may want to make their dog’s meals themselves.
The homemade dog food movement stems partially from the same motivations behind the human homemade and farm-to-table food movements – a desire for more natural, less processed, and more customizable meals. Just as some people want to know exactly what’s going into their own bodies, some dog owners feel the same way about their pets. Homemade dog food allows for control over ingredients, nutrients, and sourcing. However, it requires research and planning to formulate recipes and prepare meals that are truly balanced and healthy for dogs over the long term. This article aims to explore the key factors to weigh when considering homemade dog food.
Pros of Homemade Dog Food

One of the biggest advantages of homemade dog food is control over the ingredients. With commercial dog food, you have no way of knowing exactly what goes into each formula unless the company discloses it. However, with homemade food, you choose all the ingredients yourself. This allows you to select high-quality whole foods and avoid any fillers, by-products, artificial preservatives, or other questionable additives that are sometimes found in commercial pet foods.
Making your own dog food recipes enables you to customize the ingredients based on your dog’s specific nutritional needs. For example, you can increase or reduce the protein, fat, and carb ratios; add supplements if needed; incorporate superfoods for health; and avoid any problem ingredients that may cause allergies or intolerances in your individual dog. It also allows you to provide whole food sources of nutrients rather than synthetic vitamin supplements. With full control over what goes into your dog’s diet, you can ensure optimal nutrition tailored just for them.
Cons of Homemade Dog Food
While homemade dog food has its benefits, there are some downsides to consider as well. Two major cons are that it’s time consuming and it can be challenging to create a nutritionally balanced recipe.
Preparing homemade meals for your dog takes a significant amount of time. You need to plan recipes, shop for ingredients, prep and cook the food, and store and package individual meals. Even making a large batch may take 1-2 hours. Compared to the convenience of scooping commercial kibble from a bag, homemade dog food requires a much greater time investment.
It’s also difficult to ensure homemade food provides complete and balanced nutrition for your dog. Unlike commercial pet foods that are formulated by veterinary nutritionists, homemade recipes may be lacking in certain nutrients. Unless you consult with a veterinary nutritionist, it can be hard to guarantee you’re meeting your dog’s dietary requirements.
While homemade food comes from natural ingredients, it likely won’t provide the optimized blend of protein, fat, carbs, vitamins and minerals your dog needs. Vet-formulated foods avoid nutritional gaps that can develop with homemade recipes.
Nutritional Considerations
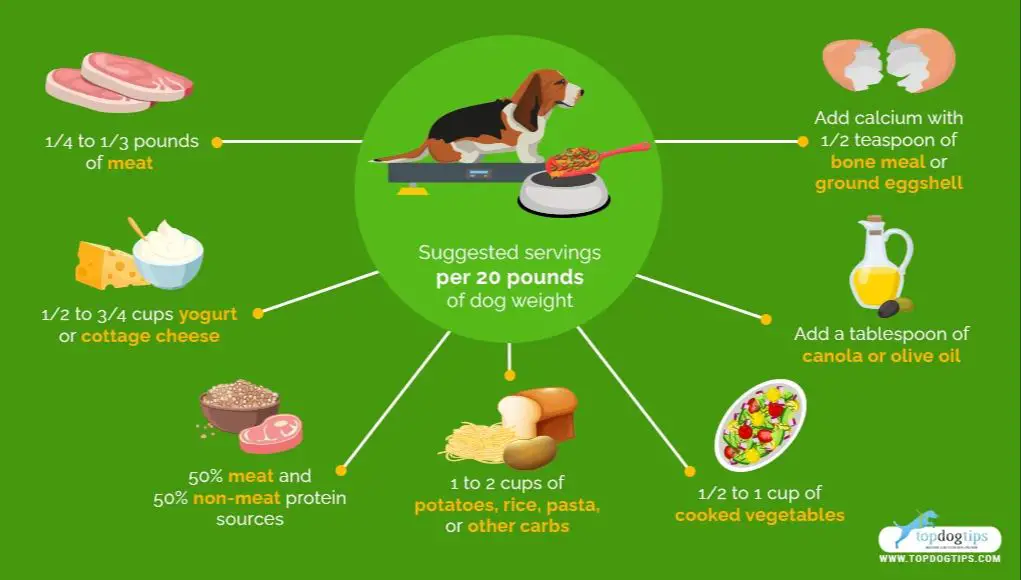
When making homemade dog food, it’s important to ensure it provides complete and balanced nutrition for your dog. There are three main nutrient categories to focus on:
Meat
Meat should make up at least 50% of the diet. Meat provides essential amino acids, vitamins like vitamin B12, and minerals like iron and zinc. Lean meats like chicken, turkey, beef or lamb are good choices. Organ meats like liver can be included in moderation as they are high in vitamin A.
Vegetables
Around 25% of the diet can consist of vegetables. Vegetables provide antioxidants, fiber, vitamins like vitamin E, and minerals like magnesium. Good options include leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, and peas. Starchy veggies like potatoes should be limited.
Grains
Whole grains like brown rice, oats or quinoa can make up the remaining 25% of calories. They provide B vitamins, fiber and carbs for energy. However, dogs have less of a need for grains than humans, so they aren’t essential if replaced with more meat and veggies.
Food Safety
When making homemade dog food, it’s important to follow food safety guidelines to avoid contamination and foodborne illness. Here are some tips:
-
Wash your hands and all cooking surfaces before preparing the food.
-
Use separate cutting boards for raw meat/fish and other ingredients.
-
Cook meat, fish, eggs thoroughly to kill any bacteria.
-
Refrigerate unused portions promptly and store in airtight containers for no more than 4 days.
-
Wash all bowls and utensils thoroughly after each use.
-
Discard any food that looks or smells spoiled.
-
Avoid cross-contaminating your dog’s food with utensils that touched your own food.
-
Freeze homemade food in serving sizes for longer storage.
Following basic food safety guidelines carefully will help prevent foodborne illnesses when preparing homemade dog food.
Recipe Development
When developing homemade dog food recipes, it’s important to consult your veterinarian, especially if your dog has any health conditions or dietary restrictions. Vets can provide guidance on your dog’s nutritional needs and recipe formulation. Start with simple recipes using a few ingredients before trying more complex recipes. Focus on quality lean proteins, digestible carbohydrates, and bioavailable vitamins and minerals.
Storage and Feeding
Proper storage of homemade dog food is critical to avoid spoilage and bacterial contamination that could make your dog sick. Prepared meals should be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 3-5 days, or can be frozen for up to 3 months. Allow frozen meals to thaw in the refrigerator before feeding.
When transitioning your dog to a homemade diet, do so gradually over the course of 5-7 days. Start by replacing 25% of their current food with the new homemade meals. Slowly increase the ratio over the week until your dog is eating 100% homemade food. This allows their digestive system to adapt and reduces the risk of gastrointestinal issues. Monitor your dog’s appetite, energy levels, stool consistency, and any other signs of reaction during the transition. If any problems arise, slow the transition period.
Cost Comparison
When evaluating the cost of homemade dog food versus commercial dog food, the main factors are the ingredients and the amount of food needed to meet your dog’s calorie and nutrition requirements. Some key considerations for cost comparison include:
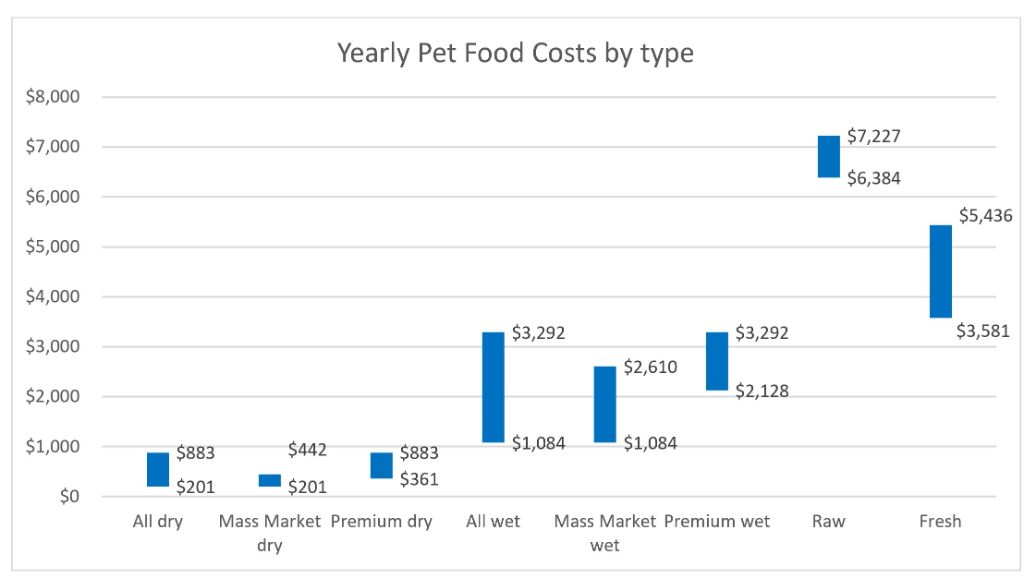
Homemade dog food can be less expensive if you utilize inexpensive ingredients like grains, beans, and in-season vegetables and fruits. However, meat is the largest expense for homemade dog food, and high quality sources of protein like lean cuts of beef, chicken, turkey, fish, etc. can make homemade food more expensive than many commercial brands.
Commercial dog foods have the benefit of buying ingredients in bulk at wholesale prices and producing food on a mass scale. This allows them to offer kibble and canned foods for a relatively low cost per pound or can.
Homemade dog food recipes must be nutritionally balanced and may require vitamin supplements to meet all nutritional needs. These supplements add to the cost of homemade food.
The amount of food a dog needs varies based on their age, breed, activity level, health status, and metabolism. Larger or active dogs will require more food and thus higher costs for either homemade or commercial dog food.
Homemade food may reduce feeding costs if you have a small dog ornotice less food is needed compared to commercial kibble diets. However the cost comparison needs evaluation on a case by case basis.
Lifestyle Factors
When deciding whether or not to make your own dog food at home, consider how it will fit into your lifestyle and daily routine. Making homemade dog food takes more time and effort compared to opening a bag or can of commercial pet food.

Some key lifestyle factors to consider include:
-
Time Commitment – Preparing homemade meals will add more tasks to your weekly meal prep. Between shopping for ingredients, following recipes, pre-portioning meals, and storing and re-heating food, you’ll need to dedicate extra hours in the kitchen.
-
Dog Preferences – Consider your dog’s appetites and tastes. Some dogs may not like the homemade recipes you prepare as much as their usual commercial dog food. Be prepared to experiment with different recipes and ingredients if your dog turns up its nose at some homemade meal iterations.
-
Travel and Vacations – Bringing homemade food on trips or leaving homemade meals for boarding or pet sitters will take more planning compared to grabbing a bag of kibble off the shelf.
Take stock of your schedule and lifestyle before committing to homemade dog food. The extra work may not fit conveniently into everyone’s routine despite the health benefits.
Conclusion
In deciding whether to make your dog’s food at home or purchase commercial dog food, there are pros and cons to consider for both options. Homemade dog food allows you to control the ingredients, which is ideal if your dog has food allergies or sensitivities. However, it requires more time and effort on your part to develop nutritionally balanced recipes and prepare the food. Commercial dog foods provide complete and balanced nutrition in a convenient form, though you have less control over the ingredients. Costs can be comparable between the two options. Lifestyle factors like your schedule and dog’s health play a role as well. Weighing all these factors can help determine if homemade or commercial food is right for your dog. The most important thing is ensuring your dog receives proper nutrition from high quality ingredients, whether his meals come from your kitchen or a bag.