Introduce the Topic
When deciding between a male or female dog as a pet, one consideration is which sex is easier to care for and maintain. There are pros and cons to both male and female dogs that impact how much effort they require in terms of their upkeep.
On one hand, some studies have shown that male dogs tend to be more active, territorial, and easily distracted than females. This can make them more challenging in terms of training and requiring adequate physical and mental exercise. On the other hand, female dogs go into heat cycles twice per year, which requires special care and attention during those periods.
Overall, there are good points and drawbacks for both sexes when it comes to ease of care. It is important to look at the specific needs of each sex and determine if you are able to properly care for and maintain either a male or female dog. This article will dive into the key differences between the maintenance requirements of male and female dogs.
Spaying/Neutering
Spaying a female dog is a more involved surgery than neutering a male dog. It requires removing the ovaries and uterus under general anesthesia, which carries risks. The average cost to spay a female dog ranges between $50 to $300 depending on the size, weight, and age of the dog (source). Larger dogs and older dogs often have higher spay costs.

After being spayed, female dogs require extra care during the recovery process. This includes restricting activity and monitoring the incision site for proper healing, which can take up to 2 weeks (source). There is also a risk of post-surgical complications like infections that may require additional veterinary treatment.
Overall, the spay procedure for females carries more financial costs, surgical risks, and recovery responsibilities compared to neutering males. However, spaying provides major health benefits for the dog and prevents accidental litters, so it is an important part of responsible pet ownership.
Heat Cycles
Female dogs go into heat cycles, also known as estrus cycles, where their bodies prepare for breeding and pregnancy. This involves vaginal bleeding, swelling of the vulva, and behavioral changes. According to VCA Hospitals, most dogs come into heat twice per year, although the interval varies between breeds and individual dogs. PetMD states that heat cycles typically last about 3 weeks on average, but can range from 2-4 weeks. The bleeding phase itself usually lasts 7-10 days according to WebMD.
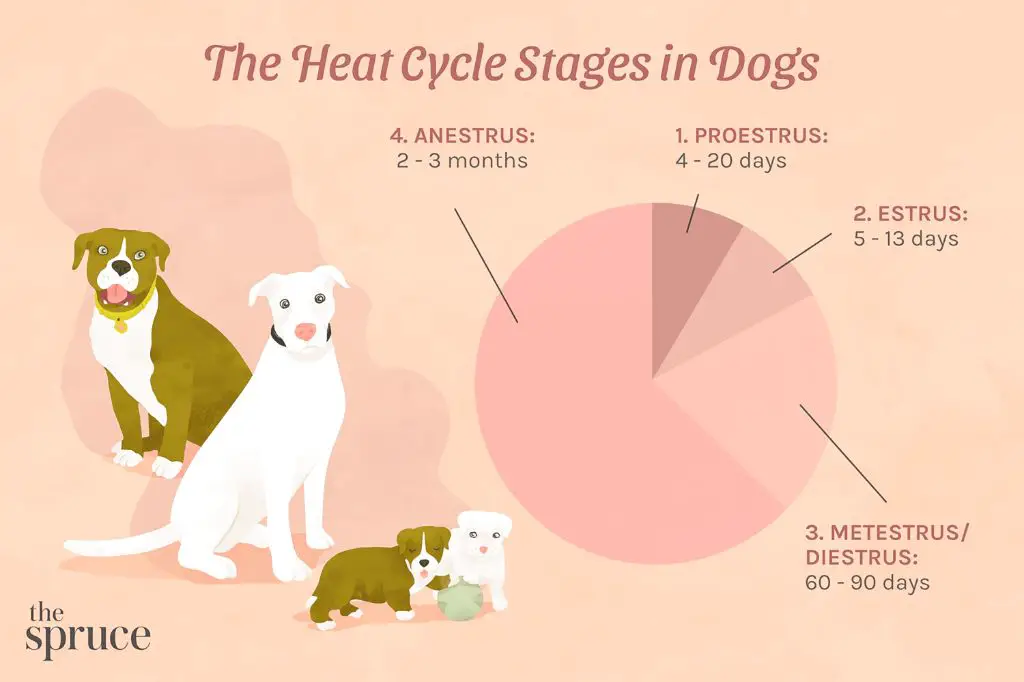
Females in heat must be monitored closely to avoid unwanted breeding. Unspayed females will attract interested males who can detect when a female is in heat from a great distance. It is important to keep females confined and away from intact males during this time. Heat cycles can create a lot of extra work for owners who must keep a close eye on their dog’s behavior and restrict her access to the outdoors.
Marking Territory
Male dogs are more likely to mark territory inside the home than female dogs. According to the AKC, even spayed females may mark territory occasionally, but marking is much more common in intact males. The reason is that males use urine marking to establish their territory and let other dogs know they are present. Intact males in particular want to leave their scent around for females in heat. Neutering can help reduce marking behaviors, but some males may continue to mark even after being neutered.

Female dogs generally do not mark territory unless they are in heat. According to WebMD, unspayed females are more likely to urine mark, especially right before and while they are in heat. This is due to hormonal changes. Spaying a female dog can eliminate this territorial marking behavior.
Overall, male dogs exhibit marking behaviors more frequently than females, especially intact males. Neutering males and spaying females can help reduce territorial marking, but some dogs may continue the behavior even after being fixed. However, intact males are the most likely to mark territory inside the home.
Roaming
One of the biggest differences between male and female dogs is that unneutered males are more likely to roam and try to escape in order to find a mate. This strong urge to roam makes them more difficult to contain, and they will often go to great lengths to get out of yards or homes. According to Rover, “An unneutered male is motivated by one thing: finding a female dog to mate with. Nothing will stop him from tracking a female dog in heat—not a leash, a fence, or even a closed door.”
Female dogs that are not spayed do go into heat cycles where they will attract male dogs, but they are not driven to actively roam and escape like males are. So if you want a dog that is easier to contain at home, a female may be a better choice. However, by neutering males and spaying females, the roaming urge can be dramatically reduced in both genders.
As the article on Insider notes, “Un-neutered male dogs can also be more prone to roaming than female dogs.” Keeping your dog secure is an important part of being a responsible owner, so the roaming factor should be considered when choosing between a male or female pup.
Aggression
Male dogs tend to be more aggressive and dominant compared to females. This is due to testosterone, which drives dominance and territorial behaviors. Intact male dogs are especially prone to aggression toward other male dogs as they seek to establish dominance.
According to a study by the shelf.guide, male dogs were 6 times more likely to show aggression toward family members, strangers, and other dogs. Neutering can reduce aggression and roaming in male dogs.
Female dogs tend to be less aggressive overall and easier to train due to their lower drive for dominance. However, some female dogs can show aggression too, especially if not spayed. Unspayed females may become aggressive toward other female dogs while in heat.
Training
Many dog owners and trainers believe females are generally easier to train and more eager to please than males. According to one source, “Females tend to be more sensitive than males & seem more eager to please their owners & to avoid friction with other dogs. They are usually quicker to learn than males.” (Source) This is likely due to hormonal differences, as female dogs tend to be less territorial and aggressive. Their desire to avoid conflict can make them more attentive and focused during training. However, individual personalities vary greatly, so the sex should not be the only factor when determining ease of training.

Vet Costs
On average, neutering a male dog costs less than spaying a female dog. According to sources, neutering a male dog can cost between $50-$350 depending on the vet clinic. Low-cost clinics often charge around $50-175, while full-service vet hospitals may charge $150-350 (source). On the other hand, spaying a female dog often costs $200-600 depending on the breed and vet clinic (source). Since spaying is a more complex surgery, it tends to cost more than neutering a male dog.
Male dogs may also have lower annual vet costs because they do not go through heat cycles or have the potential for pyometra, which is a serious uterine infection that requires emergency surgery and hospitalization. The average annual vet costs for a dog are around $212, but this can be higher for unspayed females due to reproductive health issues (source). Overall, neutering eliminates certain health risks in males and helps keep annual vet costs relatively low compared to unspayed females.
Grooming
When it comes to grooming needs, there are some differences between male and female dogs. Females tend to require more frequent grooming, especially when not spayed. Intact female dogs go through heat cycles every 6-8 months, during which time they shed heavily and require extra coat care to keep clean. The influx of hormones causes their coats to become thicker and fuller during this time. Frequent brushing and bathing is often needed.https://blog.tryfi.com/male-dogs-vs-female-dogs-which-one-is-right-for-you/
On the other hand, neutered male dogs require less grooming overall. They typically have shorter coat growth cycles and do not experience hormone fluctuations that increase shedding. However, the grooming needs of any dog depends largely on breed, coat type, and other individual factors. Short-haired dogs or breeds with hair coats rather than fur may require only occasional brushing and bathing for either gender.
Summary
In summary, there are various pros and cons to consider when choosing between a male or female dog. The main differences include:
- Females typically have heat cycles 2 times per year, which can attract male dogs. However, spaying can prevent this.
- Males are more likely to mark their territory and roam in search of females. Neutering reduces these tendencies.
- Males may be more aggressive, especially toward other males. Proper training and neutering can minimize aggression.
- Females often have lower vet costs since spaying is cheaper than neutering.
- Grooming needs depend on the breed. Some females shed more during heat cycles.
There are also many similarities between male and female dogs in terms of potential for training, socialization needs, exercise requirements, and more. Consider your lifestyle and needs when choosing between a male or female.